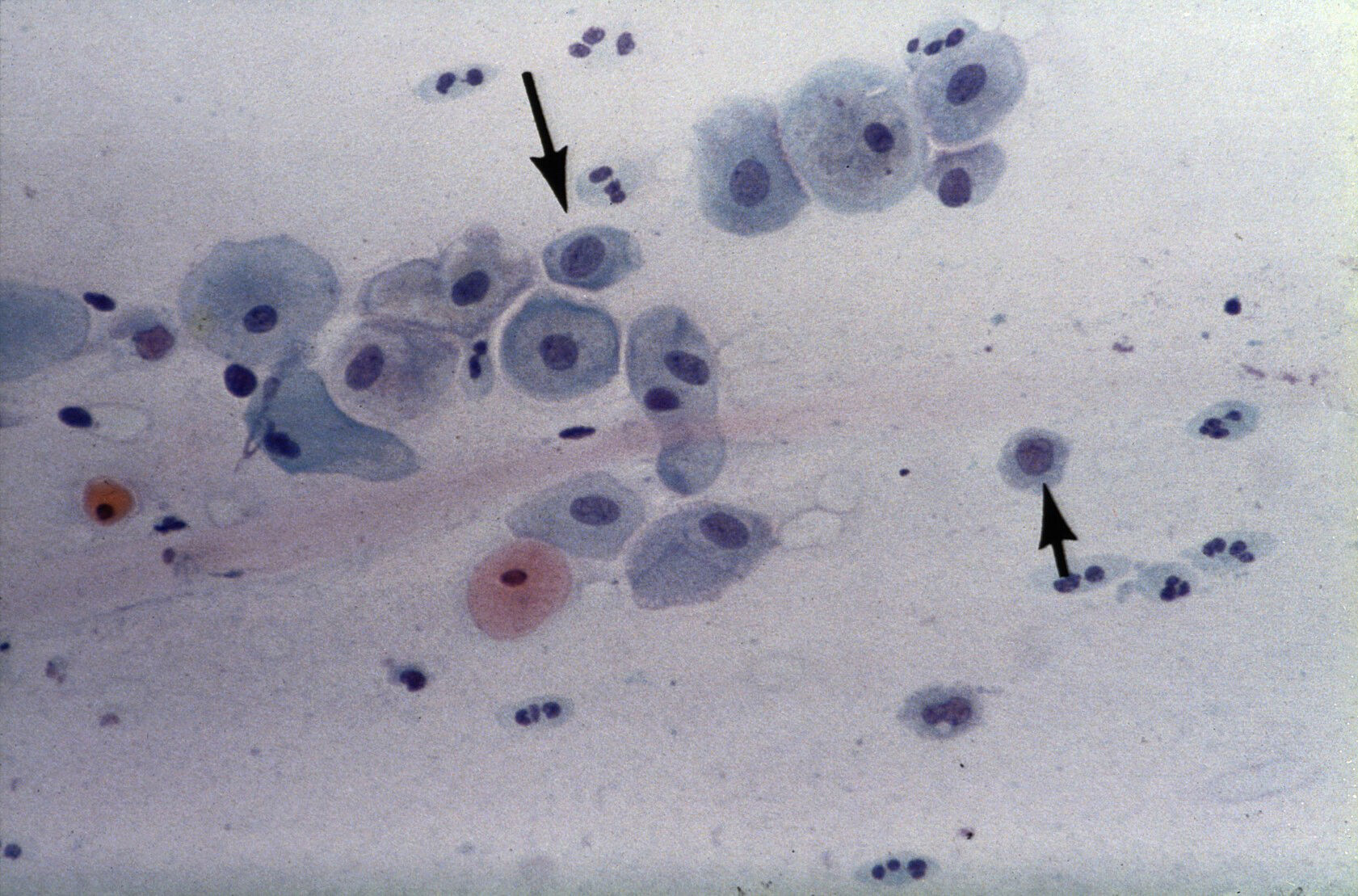
Atrophic Pattern Predominantly Parabasal Cells
Atrophic Pattern Predominantly Parabasal Cells - Web atrophic pattern histologic findings demonstrate decreased superficial squamous cells, increased parabasal cells, decreased lactobacilli. Web a pap test is a procedure used to collect cells from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) so they can be looked at closely in a lab under a microscope. However, there are normal to low numbers of neutrophils. Web hyperchromatic crowded groups in pap smear with atrophic cellular pattern with occasional atypical degenerated enlarged parabasal nucleus in some of the cells in hyperchromatic crowded groups of parabasal cells. A doctor has provided 1 answer. My gyn called & said my pap smear results were atrophic. Web up to 40 percent of postmenopausal women have symptoms of atrophic vaginitis. Occasionally in our experience, a mixed pattern composed of parabasal, intermediate, and superficial cells can be seen. Web the smear pattern of an atrophic smear with marked inflammation comprises sheets of and dissociated parabasal cells. Web vaginal atrophy is a collection of symptoms—including vaginal dryness, dysuria, and vulvovaginal irritation and itching—that are generally associated with declining estrogen levels attributable. This means no cell changes were found. It means it looks like your cells could be abnormal. My gyn called & said my pap smear results were atrophic. Web a doctor has provided 1 answer. It means that some of the cells from a pap smear did not look entirely normal but did not meet the diagnostic criteria for a lesion (meaning an area of abnormal tissue). Web the main purpose of the pap test is to prevent cervical cancer. This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among other symptoms. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). However, there are normal to low numbers of neutrophils. Loss of fragile cytoplasm of the thin atrophic and relatively dry epithelium leads to plenty bare nuclei throughout the smear. An intermediate pattern between the two is also encountered; Web up to 40 percent of postmenopausal women have symptoms of atrophic vaginitis. This may be accompanied by abundant neutrophils. The condition also includes urinary tract problems such as urinary tract infections (utis) and urinary incontinence. This is composed predominantly of intermediate cells admixed either with some superficial or parabasal cells. It means that some of the cells from a pap smear did not look entirely normal but did not meet the diagnostic criteria for a lesion (meaning an area of abnormal tissue). Cells have high n/c ratio but uniform chromatin. My gyn called & said my pap smear results were atrophic. This could be because of an infection, such as. Web the presence of degenerating parabasal cells, necrotic background, and pseudoparakeratosis were equally important in arriving at a correct interpretation of atrophic vaginitis (p <.001). Web a recognizably atrophic pattern, composed of thick clusters of intermediate and large parabasal cells, was termed “crowded” by koss. Web the main purpose of the pap test is to prevent cervical cancer. This means. An intermediate pattern between the two is also encountered; Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). My gyn called & said my pap smear results were atrophic. This is composed predominantly of intermediate cells admixed either with some superficial or parabasal cells. It only means that the organ less. For many women, vaginal atrophy not only makes intercourse painful but also leads to distressing urinary symptoms. Web vaginal atrophy is a collection of symptoms—including vaginal dryness, dysuria, and vulvovaginal irritation and itching—that are generally associated with declining estrogen levels attributable. She stated that this meant that she didn't collect enough cells & i have to have another test?: The. Web a pap test is a procedure used to collect cells from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) so they can be looked at closely in a lab under a microscope. Vaginal atrophy occurs most often after menopause. This means no cell changes were found. Web my pap smear (atrophic) shows predominantly parabasal cells with scattered superficial squamous cells.. This may be accompanied by abundant neutrophils. Web atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ascus) is the most common abnormal finding from a pap smear. Often, an examination under the microscope may diagnose inflammations from several microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, trichomoniasis, etc). Web vaginal atrophy is a collection of symptoms—including vaginal dryness, dysuria, and vulvovaginal irritation and itching—that are generally associated. The condition also includes urinary tract problems such as urinary tract infections (utis) and urinary incontinence. This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among other symptoms. Web what does the result in pap smear c 211 13 and smear 03 mean? Often, an examination under the microscope may diagnose inflammations from several microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, trichomoniasis, etc). It. Web a pap test is a procedure used to collect cells from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) so they can be looked at closely in a lab under a microscope. Web the main purpose of the pap test is to prevent cervical cancer. Because the condition is attributable to estrogen deficiency, it may occur in premenopausal women who. Web your pap test will come back with one of three results: Web the main purpose of the pap test is to prevent cervical cancer. For many women, vaginal atrophy not only makes intercourse painful but also leads to distressing urinary symptoms. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen).. It means it looks like your cells could be abnormal. It means that some of the cells from a pap smear did not look entirely normal but did not meet the diagnostic criteria for a lesion (meaning an area of abnormal tissue). It only means that the organ less than healthy epithelium, however, if it is from the uterus, that would be normal for your age. A shift in maturation index in the absence of significant inflammation is more accurately termed atrophic pattern. Cells have high n/c ratio but uniform chromatin. Web vaginal atrophy (atrophic vaginitis) is thinning, drying and inflammation of the vaginal walls that may occur when your body has less estrogen. Web vaginal atrophy is a collection of symptoms—including vaginal dryness, dysuria, and vulvovaginal irritation and itching—that are generally associated with declining estrogen levels attributable. This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among other symptoms. Vaginal atrophy occurs most often after menopause. A doctor has provided 1 answer. We are, therefore, primarily interested in detecting any atypical cells. Without the use of estrogen in the vagina or otherwi. She stated that this meant that she didn't collect enough cells & i have to have another test?: Web up to 40 percent of postmenopausal women have symptoms of atrophic vaginitis. Web atypical immature metaplasia associated with inflammation and atrophy is a challenge in cervical biopsy interpretation. Web the presence of degenerating parabasal cells, necrotic background, and pseudoparakeratosis were equally important in arriving at a correct interpretation of atrophic vaginitis (p <.001).Cell Atrophy
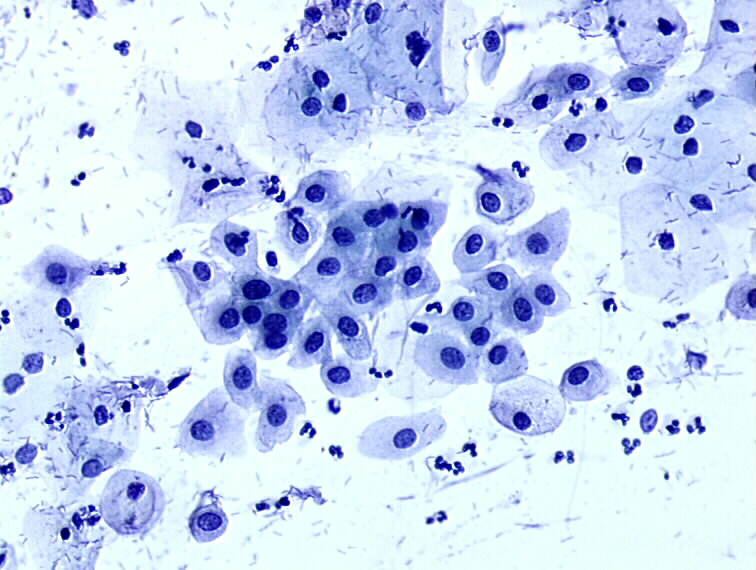
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
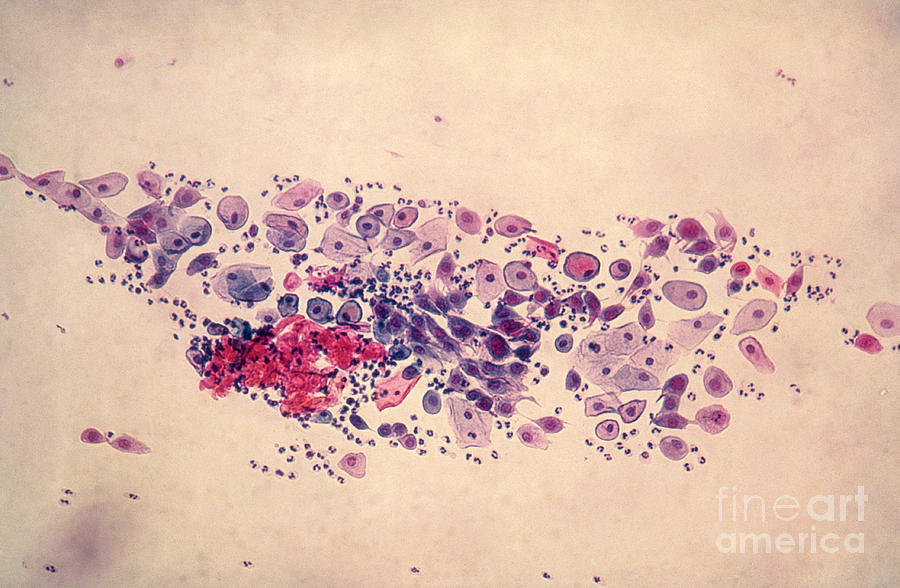
Pap Smear, Parabasal Cells Photograph by Science Source
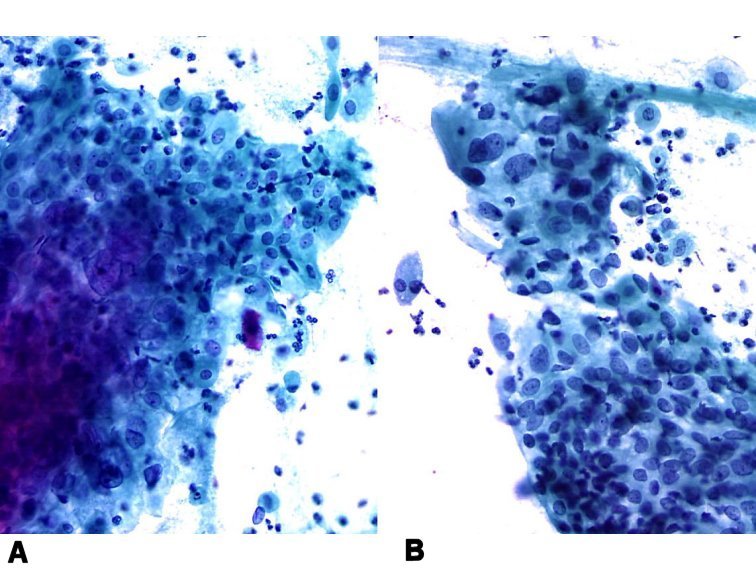
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
Histopathology and cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
Parabasal cells Collection
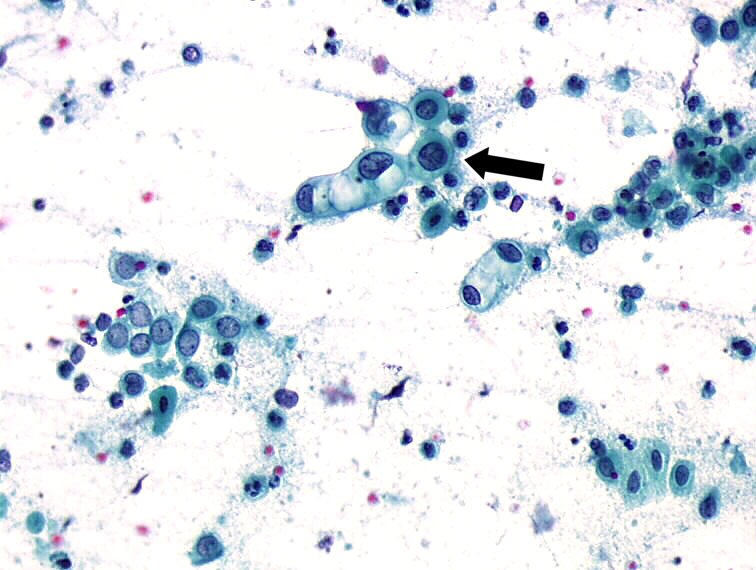
The classi¯cation of cytologic examination. (A) Parabasal cell. (B
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
Parabasal cells in pap smear with postpartum Ad , ad, cells
Because The Condition Is Attributable To Estrogen Deficiency, It May Occur In Premenopausal Women Who Take.
Web Atrophic Pattern Histologic Findings Demonstrate Decreased Superficial Squamous Cells, Increased Parabasal Cells, Decreased Lactobacilli.
Web Vaginal Atrophy Is A Condition Where The Lining Of Your Vagina Gets Drier And Thinner.
The Cells Are Evaluated For Changes That Could (But Probably Won’t) Lead To Cancer.
Related Post: