Fine Speckled Ana Pattern
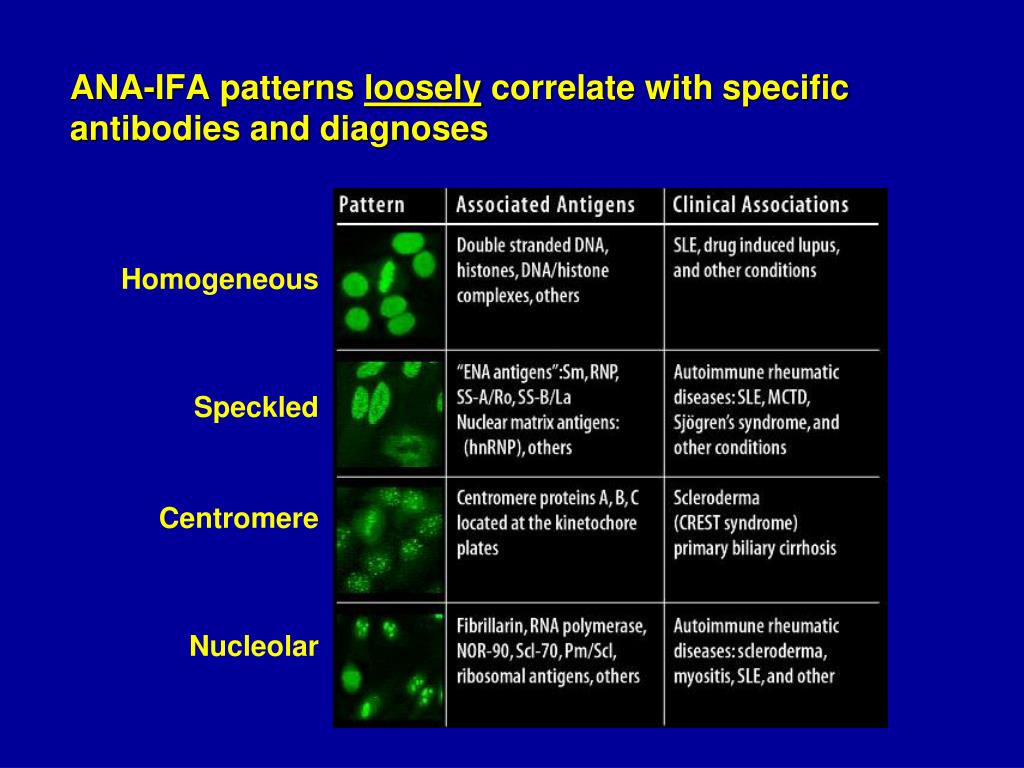
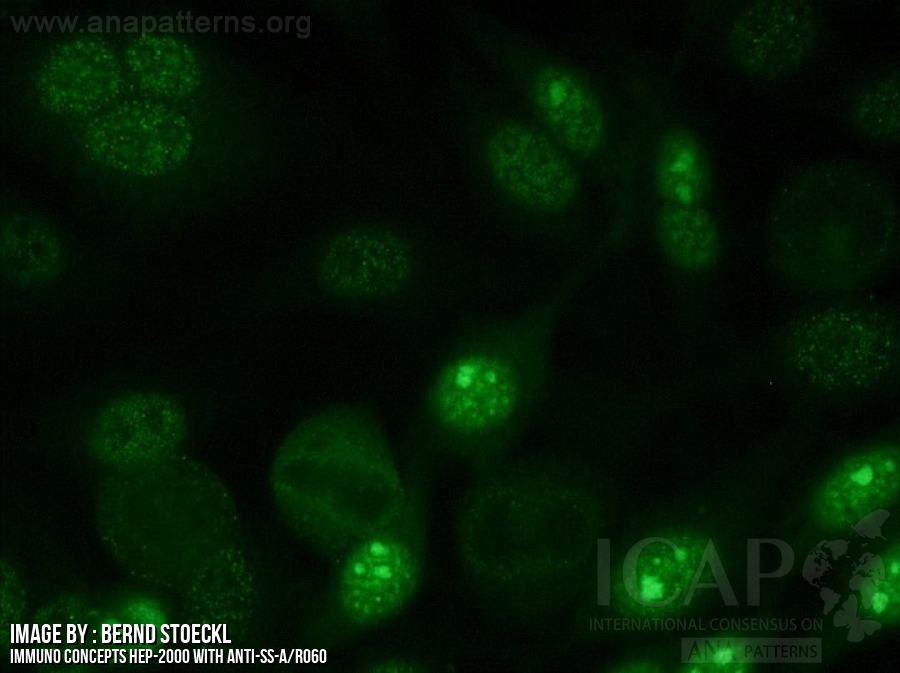
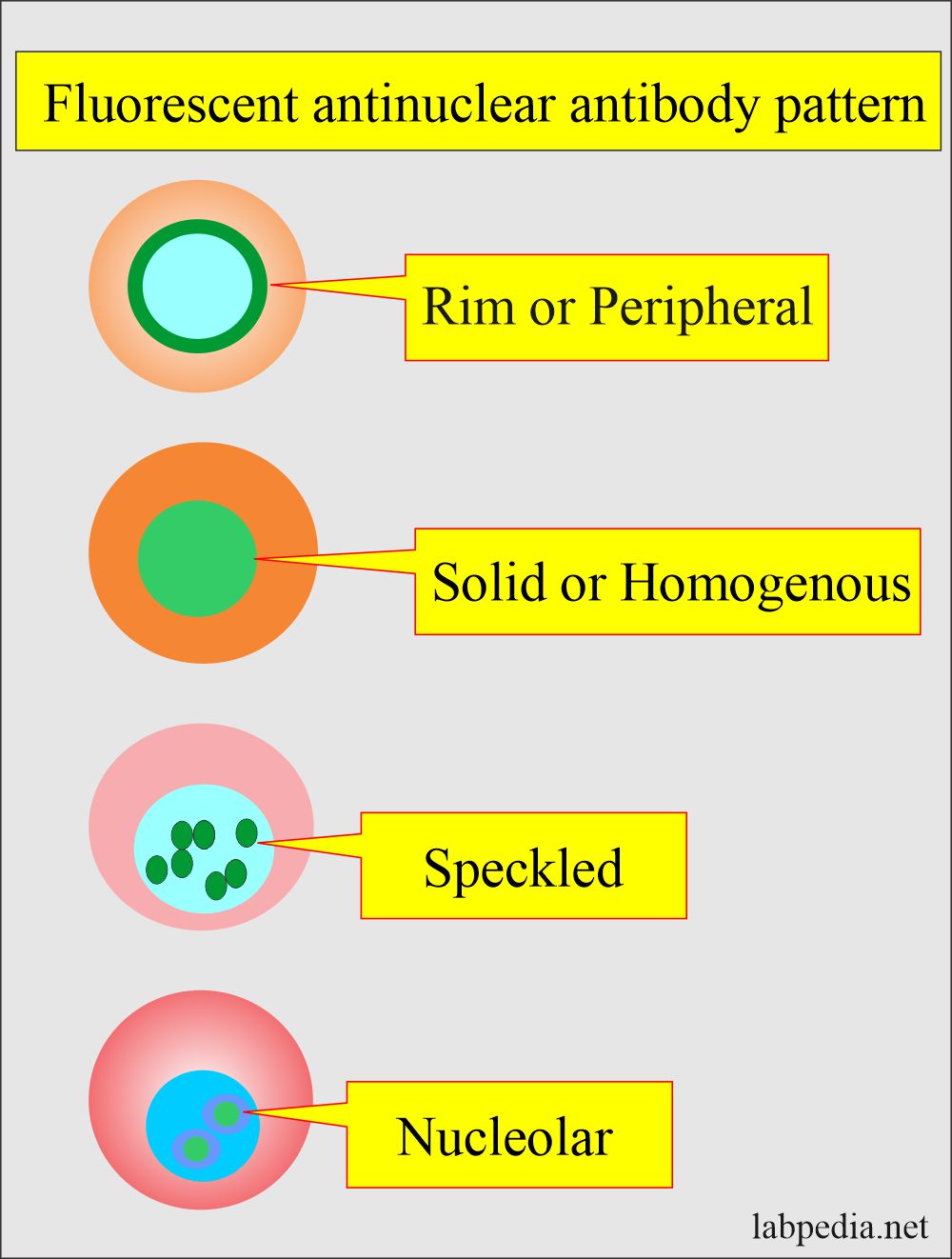
Fine Speckled Ana Pattern - Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in those with scleroderma. One pattern that deserves special attention is the dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern. Web even when detected at high titer, a positive ana result by itself (in the absence of symptoms or physical findings), does not indicate that a patient either has or will develop an autoimmune disease. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Web mixed connective tissue disease: Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. Their presence in serum may indicate an autoimmune disease. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web the dense fine speckled pattern. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in an ana test. Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated by the red arrow and the strong chromosome staining of metaphase cells by the blue arrow. While traditionally associated with autoimmune conditions, recent research suggests that this pattern may actually have a negative association with autoimmunity, particularly if it is due to an autoantibody. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Web what are antinuclear antibodies? Web a positive ana test means that you have high levels of ana in your blood. Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. Web the dfs pattern is a frequent finding (about 28% of ana positivity) in ana test using indirect immunofluorescence method. Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in those with scleroderma. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Web this topic review will cover the three broad categories of ana staining patterns: Web a positive ana test means that you have high levels of ana in your blood. Relatively high frequency of dfs pattern was observed in autoimmune diseases, contrary to the previous observations that dfs. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. Some ana appear to be unrelated to the development of autoimmune disorders. One pattern that deserves special attention is the dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern. Fine and coarse speckles of. But some people have positive ana tests even when they're healthy. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in an ana test. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Web in most cases, a positive ana test indicates that your immune system has launched a misdirected attack on. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Some ana appear to be unrelated to the development of autoimmune disorders. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. While traditionally associated with autoimmune conditions, recent research suggests that this pattern may actually have. Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated by the red arrow and the strong chromosome staining of metaphase cells by the blue arrow. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in an ana test. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard).. One pattern that deserves special attention is the dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern. Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in an ana test. But some people have positive ana tests even when they're healthy. Some ana appear to be unrelated to the development of autoimmune disorders. Web what are antinuclear antibodies? A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in those with scleroderma. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. We normally have antibodies in our blood that repel invaders in our bodies, such as viruses and bacteria microbes. Ana pattern is almost always speckled. Web in. Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. A positive ana test is usually reported as both a ratio (called a titer) and a pattern, such as smooth or. Some ana appear to be unrelated to. Ana pattern is almost always speckled. One pattern that deserves special attention is the dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Web the dense fine speckled pattern. Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in those with scleroderma. Within each of these categories, individual patterns will be defined and autoantibodies that produce the staining patterns will be identified. One pattern that deserves special attention is the dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern. Web in most cases, a positive ana test indicates that your immune system has launched a misdirected attack on your own tissue — in other words, an autoimmune reaction. Web the dense fine speckled pattern. Nucleolar — staining is seen in the nucleolus within the nucleus and is found in those with scleroderma. Relatively high frequency of dfs pattern was observed in autoimmune diseases, contrary to the previous observations that dfs pattern is not related with autoimmune diseases. Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated by the red arrow and the strong chromosome staining of metaphase cells by the blue arrow. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Web this topic review will cover the three broad categories of ana staining patterns: A positive ana test is usually reported as both a ratio (called a titer) and a pattern, such as smooth or. We normally have antibodies in our blood that repel invaders in our bodies, such as viruses and bacteria microbes. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Ana pattern is almost always speckled. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in an ana test. Some ana appear to be unrelated to the development of autoimmune disorders.Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado
ANA Patterns
Clinical significance of antiDFS70 antibody in antinuclear antibody
Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado
37+ Ana Pattern Nuclear Dense Fine Speckled FayneHjalte
Fine speckled ANA, AC4 from homepage of International consensus of ANA
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
37+ Ana Pattern Nuclear Dense Fine Speckled FayneHjalte
Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado
Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
Web Speckled — Staining Is Seen As Small Dots In The Nucleus And Is Found In People With Sle, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (Mctd), Scleroderma, And Sjögren’s Syndrome (An Autoimmune Disease That Causes Dry Eyes And Dry Mouth).
This Pattern Can Be Associated With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Systemic Sclerosis, Polymyositis, And Rheumatoid Arthritis.
While Traditionally Associated With Autoimmune Conditions, Recent Research Suggests That This Pattern May Actually Have A Negative Association With Autoimmunity, Particularly If It Is Due To An Autoantibody.
A Speckled Staining Pattern Means Fine, Coarse Speckles Of Ana Are Present Throughout The Nucleus.
Related Post: